Product Overview
The Automated Drone Image Analysis Tool (ADIAT) is a desktop application featuring a suite of algorithms designed to programmatically identify “areas of interest” in digital videos and images. The primary use case for this tool is to assist in analyzing photos taken by UAVs during search and rescue (SAR) operations, although the detection algorithms are applicable across many fields. Given that search teams often operate in austere conditions, ADIAT was built to run without requiring internet connectivity.
Development of ADIAT began in 2017 to support TEXSAR with input from industry experts. Since its first public release in 2019, ADIAT has continually evolved, adding a user-friendly user interface, major performance upgrades, new algorithms including AI-based person detection, and expanded compatibility. With the release of version 2.0, ADIAT now includes real-time streaming analysis, a redesigned image analysis guide, multi-range color detection tools, enhanced anomaly and motion detection, an upgraded AI person detector trained on a larger dataset, and stronger thermal, GPS, and mapping capabilities. The main image viewer has also been expanded with gallery and map modes, precision measurement tools, richer AOI creation and filtering options, and direct integration with CalTopo for exporting coverage and areas of interest. These updates further enhance ADIAT’s capabilities for both image and video analysis in the field.
This tool was developed as an open-source project for the SAR community, sponsored by TEXSAR (Texas Search and Rescue).
If you’re interested in contributing to the project, please reach out to us at adiat@texsar.org or check out the source code on GitHub.
Downloads
Version 2.0
Released December 8, 2025 | Last Update January 7, 2025
Image Analysis Interface Guide
The ADIAT interface is comprised of three main components: the “Setup Guide” which provides a step-by-step workflow for setting up analysis, the “Image Analysis Window” where the user can directly provide the inputs required to run the detectors, and the “Image Viewer” where the user will be able to see and interact with images that were identified as having areas of interest (AOI). Once the detection algorithm has run, the augmented images with AOIs can also be exported from the Image Viewer.
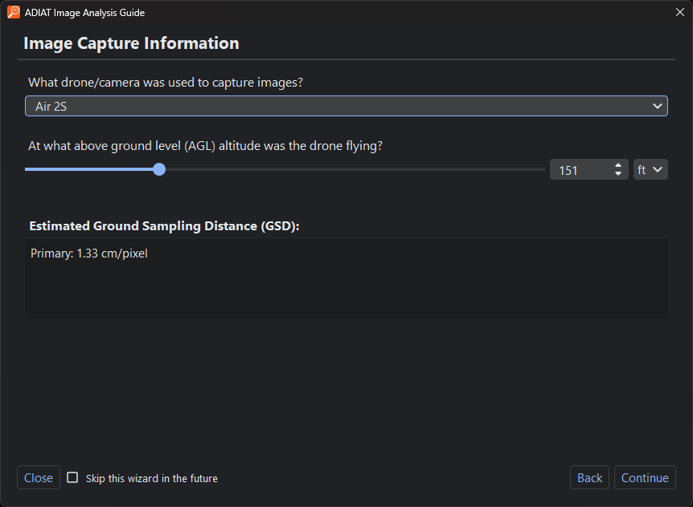
Setup Guide (Wizard)
The Image Analysis Setup Guide provides a structured approach to configuring ADIAT for image analysis. In some steps, such as the Image Capture Information screen shown below, default values are populated automatically based on metadata extracted from the image files. In other steps, information is collected through a sequence of configuration prompts to ensure alignment with the intended analysis objectives. When the setup process is complete, the collected configuration values are applied to the analysis settings and ADIAT begins image processing.
- Parameter Configuration: Analysis configuration questions and inputs.
- Close: Closes the guide and opens the Image Analysis Window for manual configuration.
- Skip this wizard in the future: When checked, the setup guide will no longer be shown when the user enters Image Analysis mode. The setup guide can still be accessed via the menu in the Image Analysis Window.
- Back: Returns to the previous step in the guide.
- Continue: Moves to the next step in the setup guide.
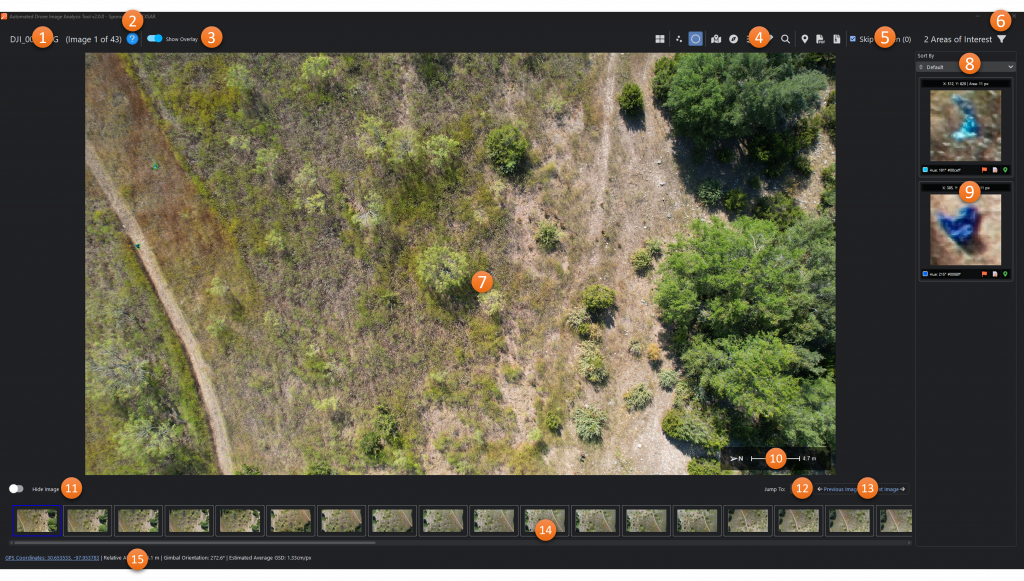
Image Analysis Window
- Menu Bar: Provides access to application configurate and navigation links as well as help resources.
- Input Folder: Location from which images will be sourced.
- Output Folder: Location where augmented images with areas of interest identified will be stored along with an xml file containing metadata from the processing.
- Min Object Area (px): The minimum size (area), in pixels, that an object must meet or exceed to be reported as an area of interest.
- Max Object Area (px): The maximum size (area), in pixels, that an object can be to be reported as an area of interest.
- No max limit: Disables the max object area parameter.
- Object Identification Color: The color that will be used to circle areas of interest.
- Max Processes: The number of images that will be processed in parallel. This number is driven by the complexity of the algorithm/features being used and the performance characteristics of the user’s computer.
- Processing Resolution: Scaled resolution at which images will be processed. Reducing resolution can make processing faster but can result in fewer detections.
- Normalize Histograms: The option to adjust the lighting conditions for all input images to where they match the conditions in the reference image. See more about this feature here.
- Algorithm: The detector that will be used. More info about the available algorithms can be found here.
- Algorithm Options: Settings and parameters that are specific to the selected algorithm.
- Start: Button that starts the image analyzer.
- Cancel: Terminates the analysis in progress.
- View Results: Launches the image viewer after analysis has been completed.
- Information Window: Provides real-time updates during the image analysis process.
Image Viewer
-
- File Name and Image Count/Index: The name of the file currently being viewed along with the index of the current image and the total number of images with areas of interest.
- Help: Opens the Image Viewer help dialog
- Show Overlay: Toggles display of the direction-of-travel arrow and scale bar (see #10 below).
- Toolbar: See “Toolbar” section
- Skip Hidden: Toggles whether “hidden” images will be shown when navigation with Previous and Next buttons. Also shows a count of hidden images in the result set.
- Areas of Interest Filter*: Filters the areas of interest being displayed based on various parameters.
- Main Image Viewer: Displays the zoomable image with areas of interest circled.
- Areas of Interest Sort*: Sorts the areas of interest based on various parameters
- Area of Interest (AOI) List*: A scrollable section showing thumbnails of areas of interest found in the image. Clicking on a thumbnail will zoom the main image to that area. Each AOI can also be flagged, have comments added for report and export purposes, or provide an estimated location based on the drone location and GSD.
- Overlay: Shows the drone orientation when the image was taken and a scale based on GSD calculated from the relative altitude.
- Hide Image: Toggles visibility of the current image.
- Jump To: Provides the ability to move directly to a specific image number
- Previous Image & Next Image: Navigation buttons to move between images with areas of interest identified by ADIAT.
- Thumbnail Navigation: Scrollable area with thumbnails representing each image with areas of interest identified by ADIAT.
- Information Bar: Provides location, altitude, orientation, and estimated GSD data for the image as well as pixel-level temperature data for thermal images and color data for RGB images.
*The Area of Interest List can be toggled between single image and gallery mode on the tool bar.
Keyboard Shortcuts
Key/ Combination Function Left Arrow Navigation to Previous Image Right Arrow Navigate to Next Image Down Arrow or P Hide Current Image and Move to Next Image Up Arrow or U Unhide the Current Image Shift + F Select AOI at cursor position F Flag/unflag currently selected AOI R Show north-oriented view of current image (rotated based on bearing) H Toggle highlight pixels of interest M Open GPS map view C Enter AOI creation mode G Toggle between Gallery View (all images) and Single Image View E Upscale currently visible portion of image Ctrl + H Open image adjustments dialog Ctrl + M Open measure tool Shift + O Override altitude for all images (manually set custom AGL altitude for GSD calculations)
Toolbar
| Icon | Name | Description |
| Gallery Mode | Switches the Areas of Interest (AOI) panel from displaying AOIs for the current image to displaying AOIs for all images. In Gallery Mode, the AOI panel can expand to multiple columns. | |
| Show POIs | Highlights pixels of interest on the main image. | |
| Show AOIs | Shows or hides AOI circles in the viewer. | |
| GPS Map | Opens the interactive GPS map window to display image locations and AOIs in geographic context. | |
| North View | Rotates the image to true north based on the drone’s recorded heading. | |
| Image Adjustments | Opens the image adjustment dialog for modifying exposure, highlights, shadows, and clarity. | |
| Measure | Opens the measurement tool for calculating distances and areas within the image. | |
| Magnify | Toggles the magnifying tool to inspect fine details at the cursor location. | |
| Map Export | Opens the export dialog to generate KML files or send data directly to CalTopo. | |
| PDF Export | Generates a PDF report containing AOIs, comments, and imagery. | |
| ZIP Export | Exports images, AOI cutouts, and metadata as a ZIP archive. |
Mouse Controls
| Key/ Combination | Function |
| Left Click + Drag | Draw a rectangle to zoom to that section |
| Right Click | Pan the image |
| Middle Click | Open magnifier |
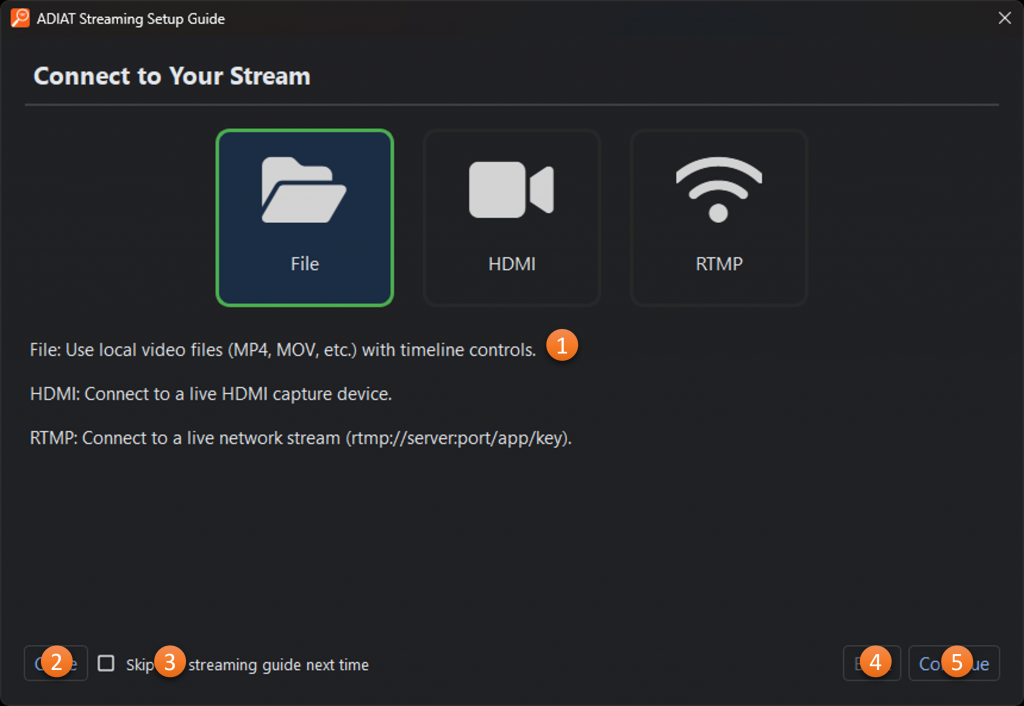
Streaming Analysis Interface Guide
Version 2.0 of ADIAT introduces streaming analysis with support for video from files, RTMP, and HDMI capture. Similar to the image analysis process, the input stream is analyzed using detection algorithms and areas of interest are highlighted for review.
Setup Guide (Wizard)
The Streaming Analysis Setup Guide provides a structured approach to configuring ADIAT for streaming analysis. Information is collected through a sequence of configuration prompts to ensure alignment with the intended analysis objectives. When the setup process is complete, the collected configuration values are applied to the analysis settings and ADIAT begins streaming analysis.
- Parameter Configuration: Analysis configuration questions and inputs.
- Close: Closes the guide and opens the Image Analysis Window for manual configuration.
- Skip this wizard in the future: When checked, the setup guide will no longer be shown when the user enters Image Analysis mode. The setup guide can still be accessed via the menu in the Image Analysis Window.
- Back: Returns to the previous step in the guide.
- Continue: Moves to the next step in the setup guide.
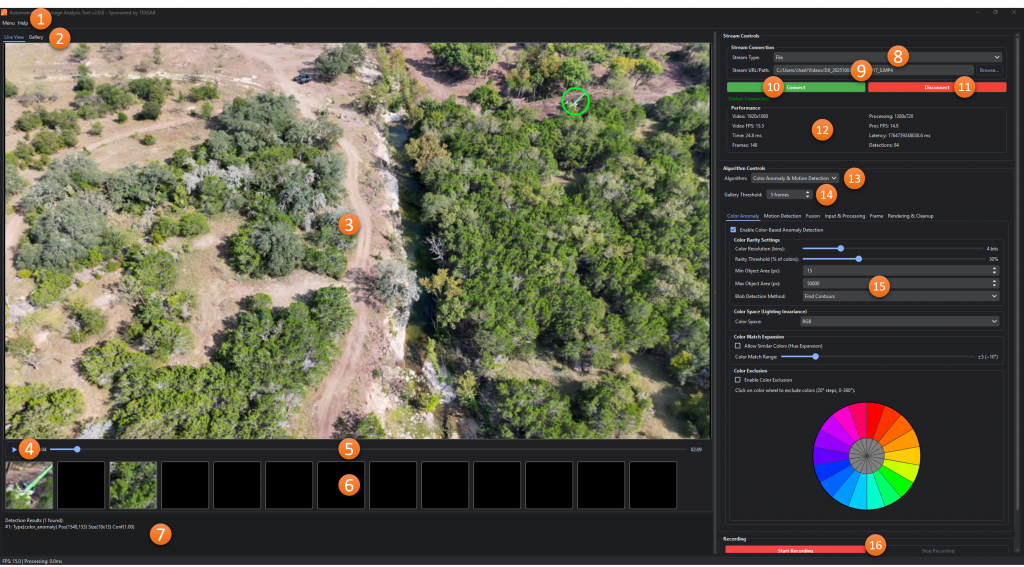
Streaming Viewer
- Menu Bar: Provides access to application configuration and navigation links as well as help resources.
- Live View/Gallery: Switches between the live view and gallery of previous detections.
- Main Video: The video stream augmented with area of interest highlights
- Play/Pause: Starts and stops the stream without disconnecting it.
- Timeline: Allows for moving forward and backward through the video (file streaming only).
- Thumbnails: Highlights showing current and recent detections
- Information Window: Provides information about detections in real-time.
- Stream URL/Path: The source for the video stream
- Stream Type: File, RTMP Stream, or HDMI Capture
- Connect: Connects to the video stream and begins playing/analyzing
- Disconnect: Disconnects from the video stream
- Performance: Performance statistics for the video and analysis
- Algorithm: The detector that will be used. More info about the available algorithms can be found here.
- Gallery Threshold: The number of frames a detection must be found in before it is added to the gallery.
- Algorithm Options: Settings and parameters that are specific to the selected algorithm.
- Recording: Controls to record the augmented video stream.
Detection Algorithms
ADIAT has been designed so that additional detection algorithms can be added as the fields of computer vision and data science continue to progress. As an open source project, users throughout the SAR and scientific communities are welcome to contribute their expertise to the project through new algorithms and refinement of those that have already been implemented.
The algorithms that have been implemented to date would not be possible without the monumental contributions other have made to freely available resources such as OpenCV, scikit-image, and Spectral Python. Wherever possible we will callout where we have leveraged these libraries as well as the contributions from additional tutorials and guides that make these resources approachable for all users.
Image Analysis Algorithms
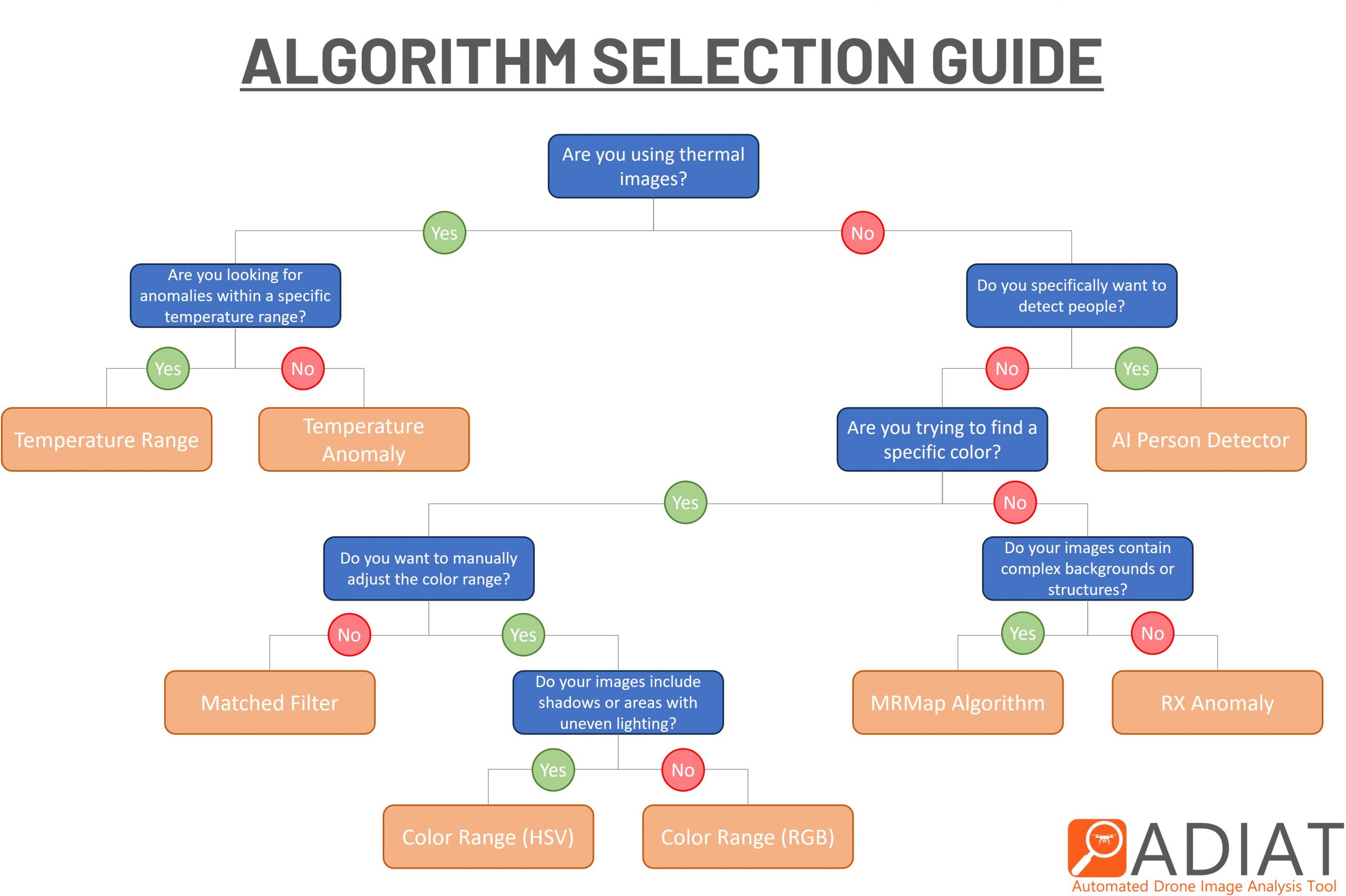
Algorithm Selection Guide
To keep ADIAT user-friendly as we add new algorithms, the following guide will help you choose the most suitable algorithm(s) for your search needs.
RGB Image Algorithms
Color Range (RGB)
Released – May 2019
Available On – Windows, MacOS
Summary
The “Color Range (RGB)” algorithm looks at each pixel in an image to determine if it is within user-specified RGB color ranges. Any sufficiently sized (defined by the user) areas where all pixels are within a selected color range are flagged as areas of interest in the image.
The color detection algorithm in ADIAT utilizes the inRange function in OpenCV.
Input Parameters
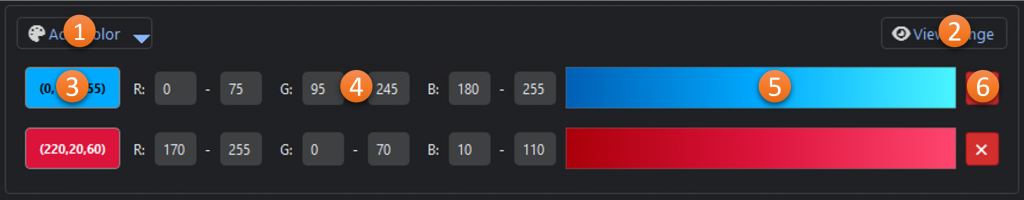
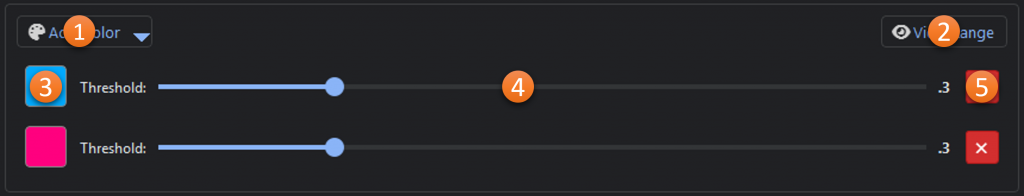
- Add Color: Dropdown menu for adding additional color ranges from a color picker, image, list, or recently used colors.
- View Range*: Shows the selected and unselected color range(s) in three color-space visualizations.
- Selected Color: The base color that was selected for the range (click to edit).
- Channel Ranges: The red, green, and blue ranges for the selected color.
- Min-Max Range: Gradient showing the range (max to min) based on the channel ranges.
- Remove: Removes the color range
*The color range viewer is a one-dimensional representation of the three-dimensional selected color range. It is intended to be a guide and is not comprehensive.
Libraries, Research, and Tutorials
Color Range (HSV)
Released – July 2025
Available On – Windows, MacOS
Summary
The “Color Range (HSV)” algorithm looks at each pixel in an image to determine if it is within user-specified color ranges. Any sufficiently sized (defined by the user) areas where all pixels are within a selected color range are flagged as areas of interest in the image.
The color detection algorithm in ADIAT utilizes the inRange function in OpenCV.
Input Parameters
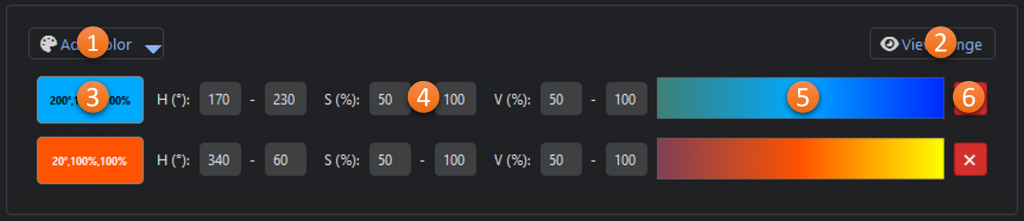
- Add Color: Dropdown menu for adding additional color ranges from an HSV color picker, image, list, or recently used colors.
- View Range*: Shows the selected and unselected color range(s) in three color-space visualizations.
- Selected Color: The base color that was selected for the range (click to edit).
- Channel Ranges: The hue, saturation, and value ranges for the selected color. Since hue is represented as a circle in HSV, the range can wrap around 360/0. In the example above the orange range is centered around 20° but goes from 340° to 60°.
- Min-Max Range: Gradient showing the range (max to min) based on the channel ranges.
- Remove: Removes the color range
* The color range viewer is a one-dimensional representation of the three-dimensional selected color range. It is intended to be a guide and is not comprehensive.
Libraries, Research, and Tutorials
Matched Filter
Released – October 2023
Available On – Windows, MacOS
Summary
With the “Matched Filter” algorithm, individual pixels are scored based on how close they are to the reference colors and then the scores are evaluated against the user-provided thresholds. Any sufficiently sized (defined by the user) areas of pixels scored above the thresholds are flagged as areas of interest in the image.
The matched filter detector used in ADIAT utilizes the matched_filter function in Spectral Python.
Input Parameters
- Add Color: Dropdown menu for adding additional color ranges from a color picker, image, list, or recently used colors.
- View Range*: Shows the selected and unselected color range(s) in three color-space visualizations.
- Selected Color: The base color that was selected for the range (click to edit).
- Threshold: Sets the minimum “score” (on a scale of .1 – 1) that we will consider to be a match to the reference color once the matched filter detector is run. Default value is .3
- Remove: Removes the color range
* The color range viewer is a one-dimensional representation of the three-dimensional selected color range. It is intended to be a guide and is not comprehensive.
Libraries, Research, and Tutorials
RX Anomaly Detection
Released – May 2019
Available On – Windows, MacOS
Summary
The RX (Reed-Xiaoli) anomaly detector extracts targets that are spectrally distinct from the image background by using the squared Mahalanobis distance as a measure of how anomalous a pixel is with respect to an assumed background. Once the RX scores have been calculated, each scored pixel is evaluated against a user-specified threshold to declare whether it should be declared anomalous. Any sufficiently sized (defined by the user) areas of pixels scored above the threshold are flagged as areas of interest in the image.
The RX anomaly detector used in ADIAT utilizes the rx function in Spectral Python.
Input Parameters
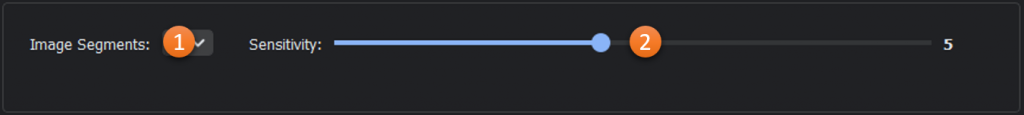
- Image Segments: Divides the image into equally-sized segments so that the target pixel will be compared to a section of the image rather than the entire image.
- Sensitivity: Threshold for determining if a pixel is anomalous with respect to the background.
Libraries, Research, and Tutorials
MRMap Algorithm
Released – February 2025
Available On – Windows, MacOS
Summary
This algorithm is inspired by a color anomaly detector used by Mountain Rescue England & Wales in their MRMap application, which was featured in Wired magazine. The algorithm simplifies the image’s colors into a manageable number of groups using a quantized histogram. It then identifies pixels with colors that are less common than a user-specified level. These anomalous pixels are then checked for proximity to other anomalous pixels, either as neighbors or within a user-defined window. Clusters of anomalous pixels exceeding a user-defined size are flagged as “areas of interest.”
Note: Given that the MRMap algorithm is more aggressive than the other algorithm when it comes to grouping pixels into anomalies, it is recommended that you set you “Min Object Area” higher than you would for other algorithms.
Input Parameters

- Image Segments: Divides the image into equally-sized segments so that the target pixel will be compared to a section of the image rather than the entire image.
- Color Space: Which color space (RGB, HSV, or LAB) should be used for analysis.
- Window Size: How many pixels away from another anomalous pixel can one be and still be considered part of the same anomaly.
- Threshold: Corresponds to the minimum of pixels in a quantized “bucket” before it is no longer considered anomalous. The threshold is programmatically adjusted based on the image size with an 8000 x 6000 pixel image set as the default reference size (i.e. if your image is 4000 x 3000 the threshold will be 50% of the value you provide since your image is half the size of the reference size.
Libraries, Research, and Tutorials
AI Person Detector
Released – July 2025
Available On – Windows, MacOS
Summary
This algorithm leverages a You Only Look Once (YOLO) object detection model that has been specifically trained to identify people in aerial imagery. Images are sliced into 1280×1280 or 2048×2048 pieces and then processed by the model. Any detections that meet or exceed the user-defined confidence threshold (that is, how confident the model is that it has found a person) are flagged as areas of interest.
Note: This model runs much faster if it can use a GPU (graphics card) to make predictions. Version 2.0 of ADIAT uses a new version of the underlying AI library which is no longer dependent on CUDA libraries.
Given that this algorithm is looking for objects (people) it is beneficial to use a higher min object area to avoid false positives.
Input Parameters
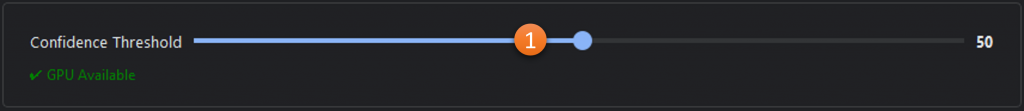
- Confidence Threshold: How sure the model must be (on a scale from 0 to 100) that the object it found is a person, before it is marked as a detection.
- GPU Check: Verification that the user’s system is set up to leverage their GPU for this algorithm.
Libraries, Research, and Tutorials
Citations
- HERIDAL – Dunja Božić-Štulić, Željko Marušić, Sven Gotovac: Deep Learning Approach on Aerial Imagery in Supporting Land Search and Rescue Missions, International Journal of Computer Vision, 2019.
- SARD – Sambolek, Marina Ivasic-Kos, “SEARCH AND RESCUE IMAGE DATASET FOR PERSON DETECTION – SARD”, IEEE Dataport, March 1, 2021, doi:10.21227/ahxm-k331
- WiSARD – Broyles, D.* and Hayner, C.* and Leung, K., “WiSARD: A Labeled Visual and Thermal Image Dataset for Wilderness Search and Rescue”, IEEE/RSJ Int.\ Conf.\ on Intelligent Robots \& Systems, 2022
- Lacmus Drone Dataset (LaDD)
Thermal Algorithms
Temperature Range
Released – August 2024
Available On – Windows
Summary
The “Temperature Range” algorithm leverages radiometric data capture by thermal sensors and determines for each pixel if it is within a user-specified temperature range. Any sufficiently sized areas where all pixels are within the selected temperature range are flagged as “areas of interest” in the jpg rendering of the thermal data.
Drones/Cameras Supported:
DJI – H20T, H30T, XT2, XTR, XTS, Mavic 2 Enterprise-Advanced, Mavic 3T, Mavic 3TD, Matrice 30T, Matrice 4T, Matrice 4TD
Autel – EVO II 640T v3, EVO Max 4T
FLIR – AX8, B60, E40, T650
Input Parameters
- Minimum Temp*: The bottom of the temperature range
- Maximum Temp*: The top of the temperature range
*The temperature unit can be set in the application preferences.
Libraries, Research, and Tutorials
Temperature Anomaly
Released – August 2024
Available On – Windows
Summary
The “Temperature Anomaly” algorithm leverages radiometric data capture by thermal sensors and determines for each pixel if it is outside of the user-specified number of standard deviations from the mean temperature of all pixels in the image. Any sufficiently sized areas where all pixels are anomalous are flagged as “areas of interest” in the jpg rendering of the thermal data.
Drones/Cameras Supported:
DJI – H20T, H30T, XT2, XTR, XTS, Mavic 2 Enterprise-Advanced, Mavic 3T, Mavic 3TD, Matrice 30T, Matrice 4T, Matrice 4TD
Autel – EVO II 640T v3, EVO Max 4T
FLIR – AX8, B60, E40, T650
Input Parameters
- Anomaly Type: Specifies if anomalies above, below, or above and below the mean should be flagged.
- Anomaly Threshold: The number of standard deviations a pixel must exceed to be considered anomalous
- Image Segments: Divides the image into equally-sized segments so that the target pixel will be compared to a section of the image rather than the entire image.
Libraries, Research, and Tutorials
Advanced Features
Histogram Normalization
Released – October 2023
Available On – RGB Image Algorithms
Summary
Lighting conditions can have a dramatic impact on the representation of colors in an image which, in turn, means that color identification can be problematic with UAV photos when they are taken at different times of day or with variable cloud cover. Histogram normalization addresses this by “standardizing” the lighting conditions across a set of images so that they can be evaluated consistently.
The histogram normalization feature in ADIAT utilizes the match_histograms function in scikit-image.
Input Parameters

- Reference Image: The image that will be used as the baseline against which all other images will be normalized.
Libraries, Research, and Tutorials
Streaming Analysis Algorithms
Common Settings Interfaces
Input & Processing Settings
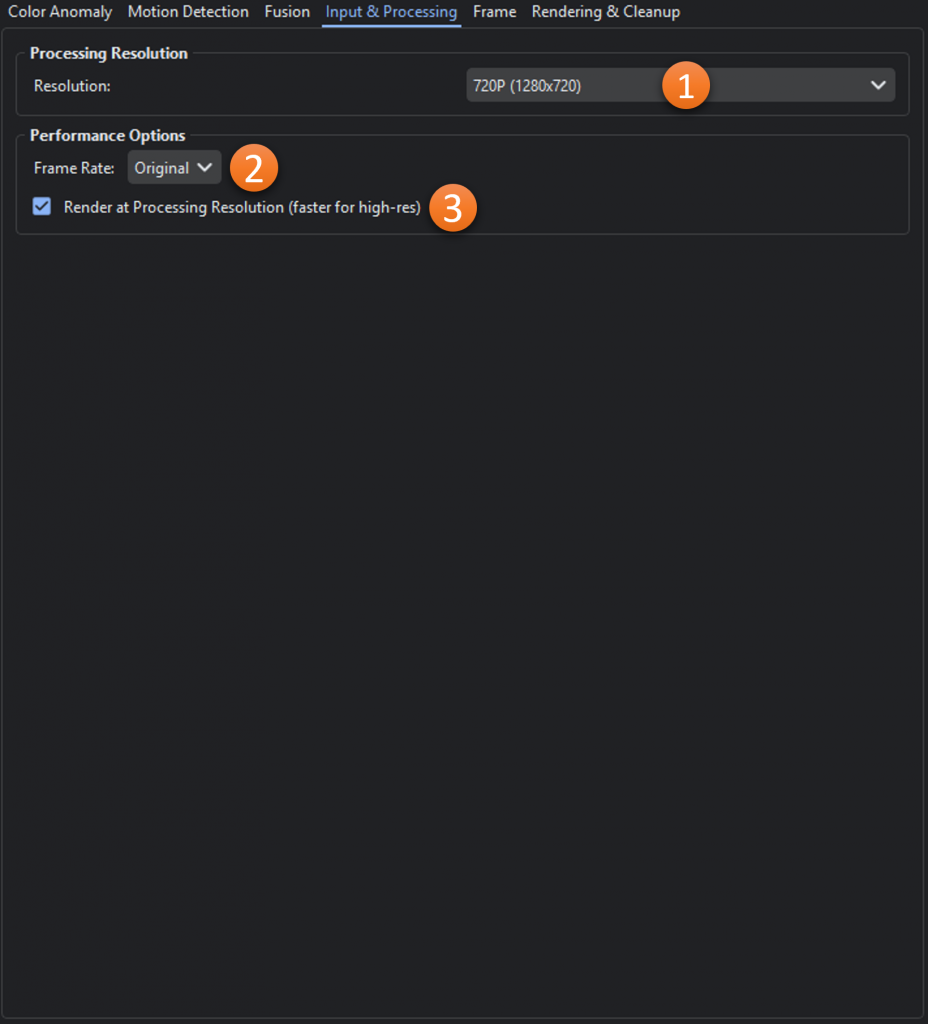
- Resolution: The resolution the video will be resized to for processing.
- Frame Rate: Limits the frame rate for processing
- Render at Processing Resolution (faster for high-res): Renders detection overlays at processing resolution instead of original video resolution. Significantly faster for high-resolution videos (1080p+) with minimal visual impact. For example, processing at 720p but video is 4K – renders at 720p then upscales. Recommended: ON for high-res videos, OFF for native 720p or lower.
Frame Settings
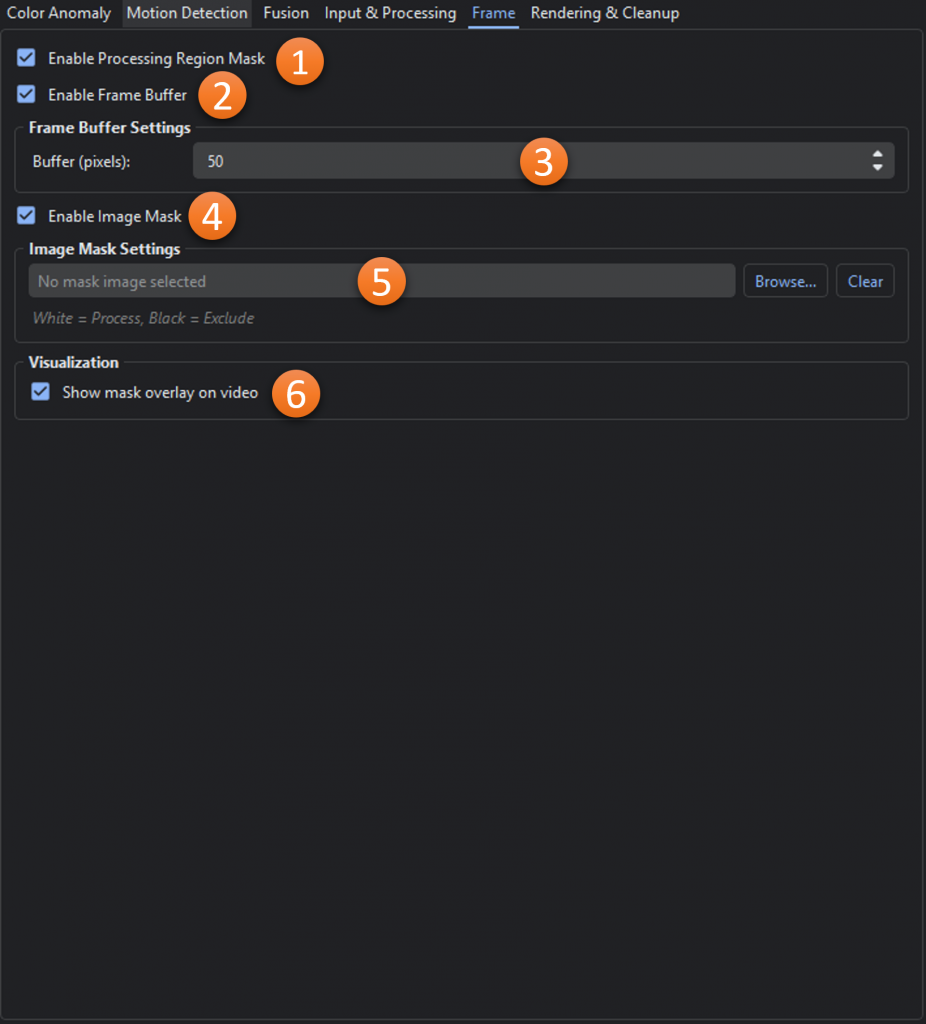
- Enable Processing Region Mask: Toggles the use of region masking
- Enable Frame Buffer: Toggles the use of the frame exclusion buffer
- Buffer (pixels): Number of pixels to exclude from all edges of the video
- Enable Image Mask: Toggles the use of a custom image mask
- Image Mask File: File to use for the image mask
- Show mask overlay on video: Toggles whether the mask overlay is shown in the video player
Rendering & Cleanup Settings

- Shape Mode: What shape should be used to highlight the areas of interest
- Show Text Labels (slower): Shows detection type, confidence, and area near each detection
- Show Contours (slowest): Draws exact pixel-precise detection boundaries
- Use Detection Color (hue @ 100% sat/val for color anomalies): Highlights the area of interest using the average color from the detection
- Max Detections: Maximum number of detections to render on screen
- Enable Temporal Voting (reduce flicker): Reduces flicker by requiring detections to appear consistently across multiple frames.
- Window Frames (M): Size of the temporal window (frames) for persistence filtering.
- Threshold (N of M): Number of frames (N) within the window (M) where motion must appear.
- Enable Aspect Ratio Filtering: Filters detections based on width/height ratio.
- Min Ratio: Minimum allowed width/height ratio.
- Max Ratio: Maximum allowed width/height ratio.
- Enable Detection Clustering: Merges nearby detections into a single detection.
- Clustering Distance (px): Maximum distance (pixels) between detection centroids to merge them
Algorithms
Color Detection
Released – December 2025
Available On – Windows, MacOS
Summary
Targets specific colors in streaming video using user-defined HSV color ranges. Any sufficiently sized (defined by the user) areas where all pixels are within the selected color ranges are flagged as areas of interest in the streaming viewer. Multiple color ranges can be added via the shared color selection system (color range picker, image eye dropper, color list, or recently used color ranges).
Color Selection Settings
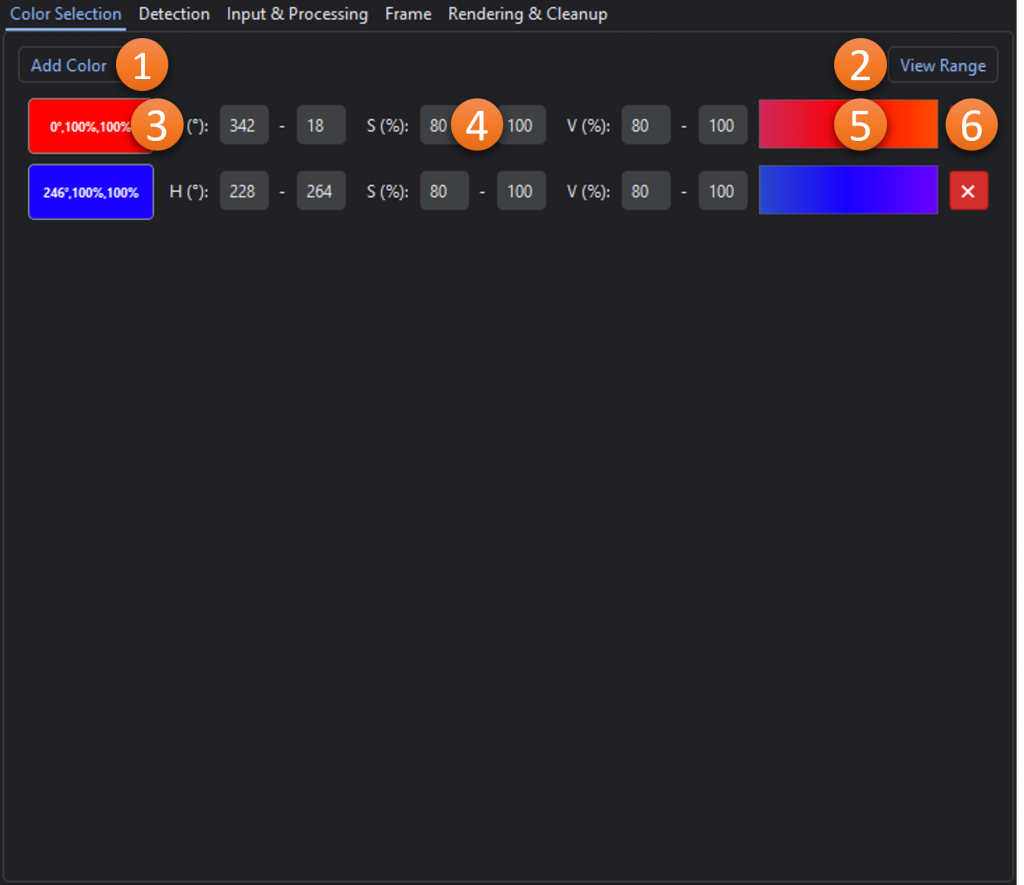
- Add Color: Dropdown menu for adding additional color ranges from an HSV color picker, image, list, or recently used colors.
- View Range*: Shows the selected and unselected color range(s) in 3 color maps.
- Selected Color: The base color that was selected for the range (click to edit).
- Channel Ranges: The hue, saturation, and value ranges for the selected color. Since hue is represented as a circle in HSV, the range can wrap around 360/0. In the example above the orange range is centered around 20° but goes from 340° to 60°.
- Min-Max Range: Gradient showing the range (max to min) based on the channel ranges.
- Remove: Removes the color range
* The color range viewer is a one-dimensional representation of the three-dimensional selected color range. It is intended to be a guide and is not comprehensive.
Detection Settings
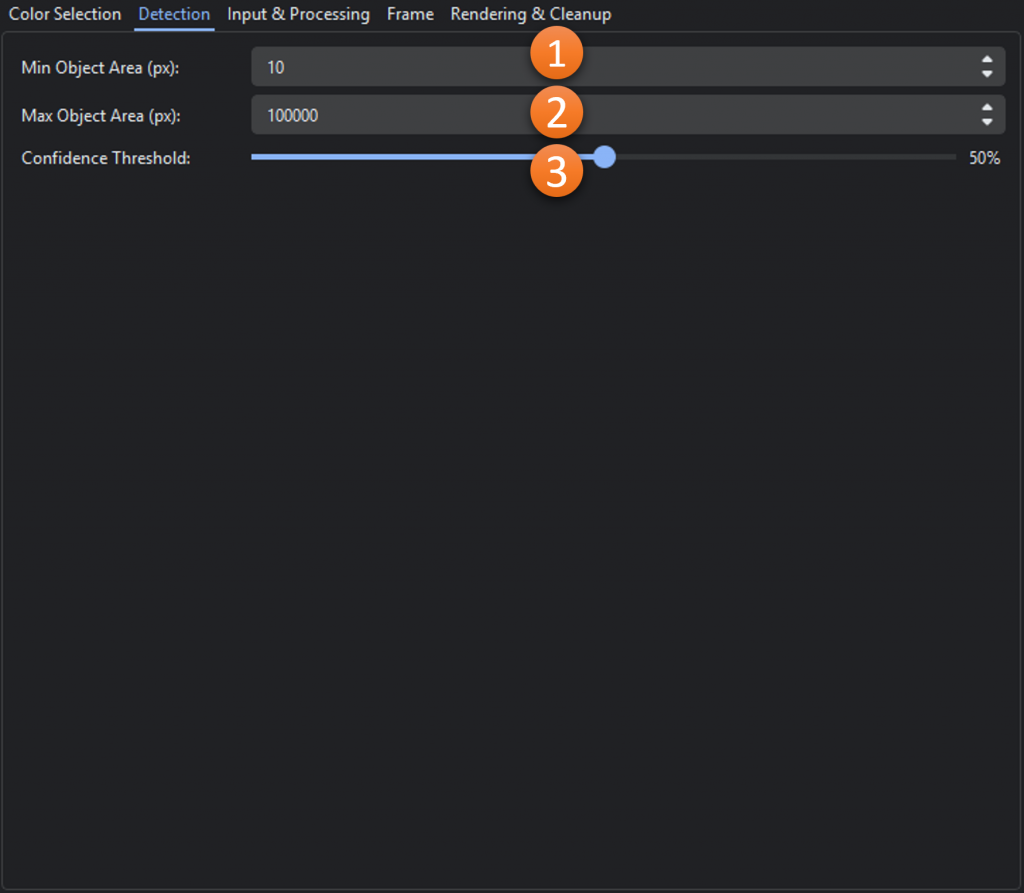
- Min Object Area (px): The minimum size (area), in pixels, that an object must meet or exceed to be flagged as an area of interest.
- Max Object Area (px): The maximum size (area), in pixels, that an object can be to be flagged as an area of interest.
- Confidence Threshold: The average of size score min(area / max_area, 1.0) and shape score (contour area / convex hull area). Higher values indicate well-formed and larger detections. A lower threshold will return more results but will include “weaker” detections.
Color Anomaly & Motion Detection
Released – December 2025
Available On – Windows, MacOS
Summary
Targets color and motion anomalies either separately or together in streaming videos. The color anomaly detector utilizes color quantization, like MRMap, to identify rare colors in the image. The motion detection uses any of 3 methods to identify objects in motion when the camera is stationary. The color and motion anomalies can be fused together if desired and any sufficiently sized anomalous (defined by the user) areas are flagged as areas of interest in the streaming viewer.
Color Anomaly Settings
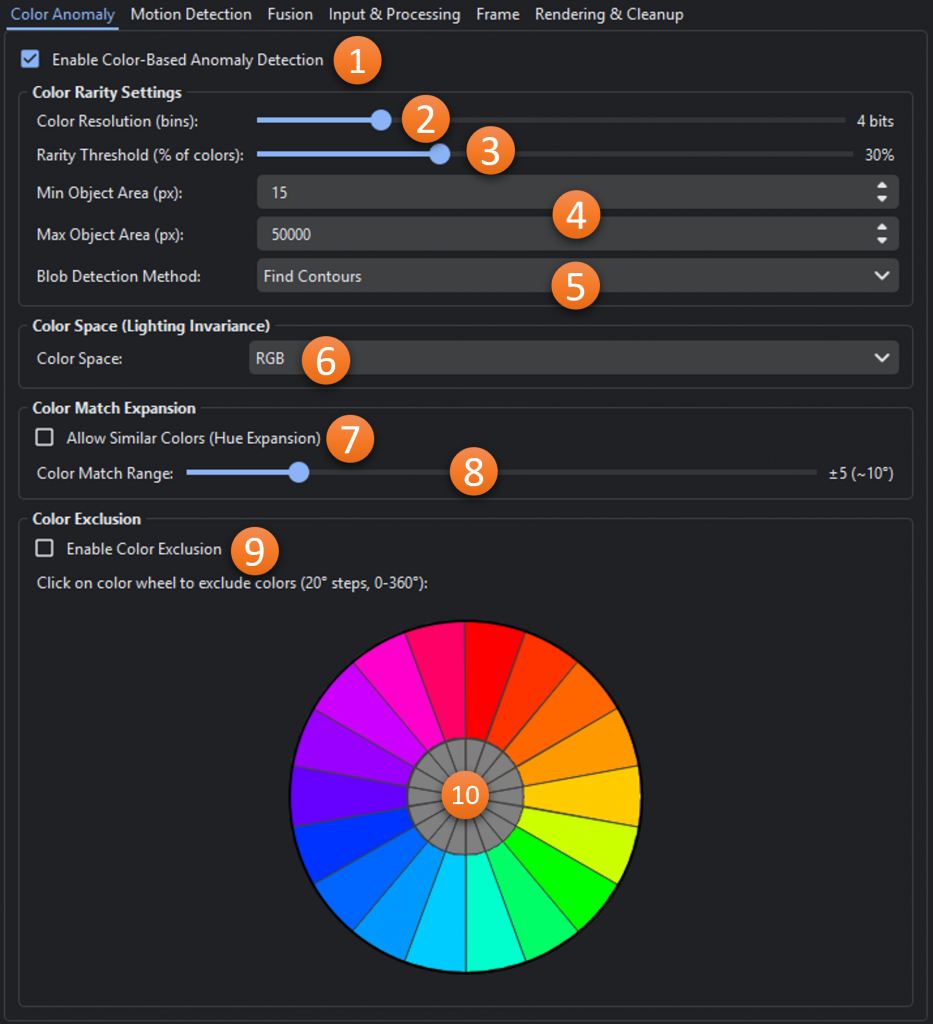
- Enable Color-Based Anomaly Detection: Toggles whether color-base anomalies should be identified.
- Color Resolution (bins): Sets the number of bins/bits for quantization. Each color channel starts as 8 bits.
- Rarity Threshold: Threshold for non-empty bins to not be considered anomalous. Lower number will result in more detections and higher number will be more selective.
- Min/Max Object Area(px): The minimum and maximum areas allowed for areas of interest
- Blob Detection Method: Method for extracting blob regions from detections
- Color Space: Which color space (RGB, HSV, or LAB) should be used for detection.
- Allow Similar Colors (Hue Expansion): Toggles the usage of hue expansion with color anomaly detection
- Color Match Range: Effectively acts as color range detector. The average hue of detected color anomalies is used as a base color and the range is set here. Any areas of the frame that are a match, and within the min/max object area constrains, are highlighted.
- Enable Color Exclusion: Toggles the exclusion of anomalies based on average hue.
- Color Exclusion Wheel: Each section in the wheel represents a 20° arc of hues. When one or more sections are enabled, any color anomalies with an average hue in those section(s) are ignored.
Motion Detection Settings
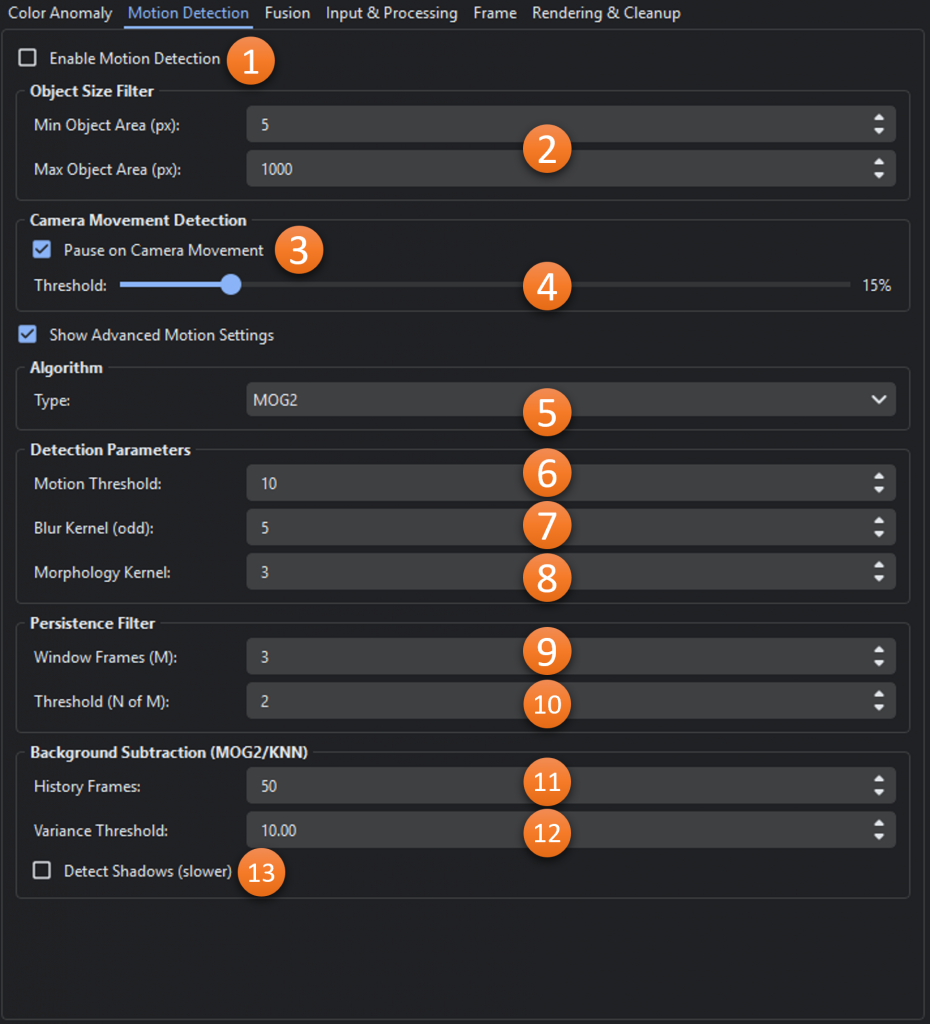
- Enable Motion Detection: Toggles whether motion-based anomalies should be identified.
- Min/Max Object Area(px): The minimum and maximum areas allowed for areas of interest
- Pause on Camera Movement: When enabled, pauses detection when camera movement is detected.
- Camera Movement Threshold: Percentage of frame pixels that must change to trigger a camera movement pause.
- Algorithm Type: Which type of motion detector should be used.
MOG2 (Gaussian Mixture Model): Good for static cameras, adapts to gradual lighting changes.
KNN (K-Nearest Neighbors): Alternative for busy scenes.
FRAME_DIFF: Simple frame differencing (baseline). - Motion Threshold: Minimum pixel intensity change (0-255) to consider motion.
- Blur Kernel (odd): Used for smoothing
- Morphology Kernel: Used for noise cleanup
- Window Frames (M): Size of the temporal window (frames) for persistence filtering.
- Threshold (N of M): Number of frames (N) within the window (M) where motion must appear.
- History Frames: Number of frames used to learn the background model.
- Variance Threshold: Threshold for background/foreground classification in MOG2
- Detect Shadows: When enabled shadows are filtered out.
Fusion Settings
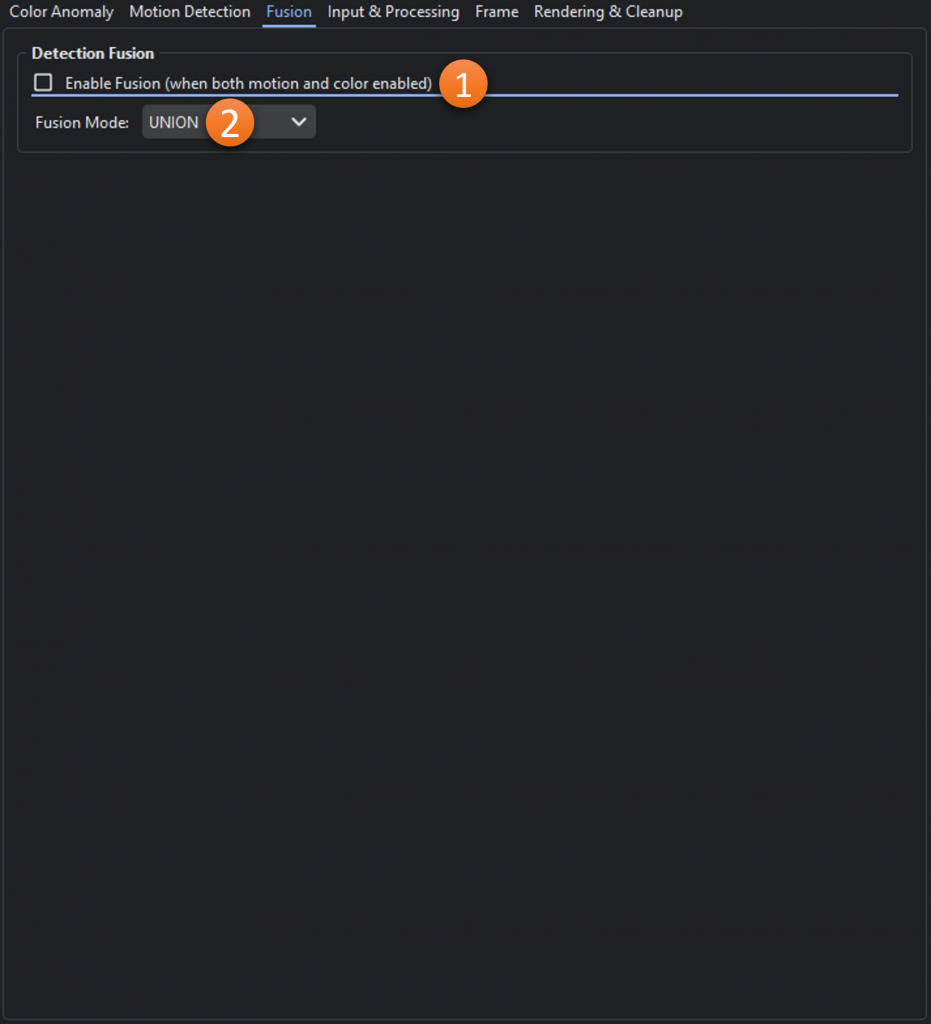
- Enable Fusion (when both motion and color enabled): Toggles whether fusion should be used for color and motion anomalies
- Fusion Mode: How motion and color detections are combined
UNION – Returns all detections from both sources. Overlapping detections (IoU > 0.3) are merged into one
INTERSECTION – Only keeps detections that appear in both motion and color (IoU > 0.3).
COLOR_PRIORITY – Starts with all color detections, adds motion detections that don’t overlap with color.
MOTION_PRIORITY – Starts with all motion detections, adds color detections that don’t overlap with motion.
Technical Details
Overview
ADIAT was built in Python and has been compiled for ease of use and packaged with an installer for portability and ease of use. As an open source program, the source code is freely available in Github along with instructions on how to run and compile the app.
The modular structure of the codebase was designed to allow additional algorithms to be added with minimal changes to the core functions. If you are interested in contributing to this project please contact us at adiat@texsar.org
System Requirements
ADIAT runs on any modern Windows or Mac system. The application can scale memory and CPU usage based on your system’s capabilities, but generally, higher performance hardware will yield faster processing times. ADIAT requires 440 MB of disk space for installation, and you’ll need additional space for any augmented images generated during use.
Due to 3rd-party library limitations, thermal algorithms are only available in the Windows version of ADIAT.
License Information
ADIAT is licensed under the GNU General Public License v3.0. This makes it freely available to use by the community with limited conditions.
Release Notes
- 2.0 (December, 2025)
- Real-Time Streaming Analysis
- Streaming video feeds from files, RTMP, and HDMI capture
- Streaming Setup Guide walks users through setup step-by-step.
- Color Detection algorithm targets color ranges selected by the user in the HSV color space
- Color anomaly and motion detection algorithms highlight areas of interest without a specific color target.
- Image Analysis
- Image Analysis Setup Guide walks users through setup step-by-step.
- All color detection algorithms (Color Range, Color Range HSV, and Matched Filter) now support searching for multiple color ranges at the same time.
- All color detection algorithms have additional color selection tools including a new, more intuitive, color range selector for HSV, eye dropper tools to select a color from an image, and a curated list of common colors for users to select from.
- RX Anomaly detector was updated to use the LAB color space for better anomaly detection.
- The underlying library used for AI detection has been switched to one that is MUCH easier for end users to be able to use (no more external dependencies that need to be installed and configured).
- The AI Person Detector model has been fully retrained with a larger training data set.
- Main Image Viewer
- Gallery mode to see the Areas of Interest (AOIs) across all images
- Map view to see images and the AOIs in context
- Magnifier, Image Orientation, Image Adjustment, and ruler tools to quickly dive deeper into images
- Additional AOI creation, sorting, filtering as well as the ability to flag and comment on individual AOIs
- AOI estimated location calculations based on camera altitude and orientation
- Significant improvements to all exports and addition of integration into CalTopo to quickly export map images, coverage, and areas of interest
- Thermal & GPS Improvements
- Thermal, temperature, and mapping support is significantly stronger:
- Improved DJI / Autel / FLIR temperature handling
- Thermal anomaly wizard enhancements
- Compass roses, bearing calculators, and combined map export
- Real-Time Streaming Analysis
- 1.6 (July, 2025)
- Added AI Person Detector Algorithm
- Added HSV version of Color Range Algorithm
- Added scale and drone orientation elements to viewer
- Updated logic for calculating object area
- 1.5 (February, 2025)
- Added MRMap Algorithm for RGB images
- Added PDF Report Generator and Zip Bundle generators to Viewer
- Added Max Object Size parameter
- Added support for DJI Matrice 4T
- 1.4 (November, 2024)
- Improved viewer experience with thumbnail navigation and show/hide capabilities.
- 1.3 (August, 2024)
- Added support for thermal images with temperature range and temperature anomaly algorithms
- Added video parser capability
- Overall performance improvements
- 1.2 (October, 2023)
- Added K-Means Clustering and Histogram Normalization features as well as Matched Filter algorithm.
- Performance and detection improvements
- Completed major refactoring and modernization of the codebase
- 1.1 (May 30, 2019)
- First public release including core platform with Color Detection and RX Anomaly algorithms.